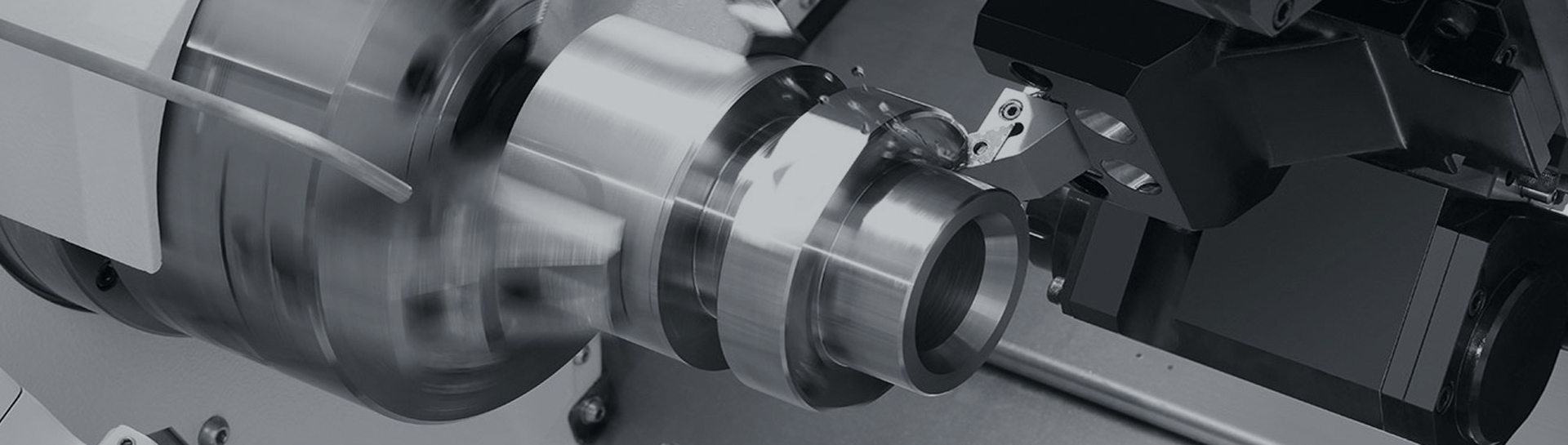
In the realm of mechanical engineering, power transmission is a fundamental process that enables the operation of countless machines, from small household appliances to large industrial equipment. At the heart of this process lies a critical component known as a coupling. A coupling is a mechanical device designed to connect two shafts together, transmitting torque from a driving shaft (e.g., from an electric motor or engine) to a driven shaft (e.g., to a pump, fan, or gearbox). Beyond mere torque transmission, couplings also accommodate misalignments between shafts, absorb vibrations, compensate for thermal expansion, and protect connected components from damage, making them indispensable in modern mechanical systems.
The primary function of a coupling is to ensure the smooth and efficient transfer of rotational power while addressing the inherent challenges of shaft connection. Shaft misalignment is a common issue in mechanical systems, arising from factors such as improper installation, structural deformation, or thermal expansion during operation. Couplings are engineered to handle three main types of misalignment: angular misalignment (where shafts are inclined relative to each other), parallel misalignment (where shafts are offset but parallel), and axial misalignment (where shafts move along their axial direction). Additionally, couplings can dampen vibrations generated by the driving source, reducing noise and minimizing wear on bearings, seals, and other critical components. In some cases, couplings also act as a safety mechanism, disconnecting shafts in the event of overload to prevent catastrophic failure.
Couplings are classified into two main categories based on their flexibility: rigid couplings and flexible couplings. Each category is designed for specific applications and operating conditions, with distinct advantages and limitations.
Rigid couplings are the simplest type of coupling, characterized by their inability to accommodate any shaft misalignment. They are used when shafts are perfectly aligned and require a rigid, fixed connection. Common types of rigid couplings include flange couplings, sleeve couplings, and clamp couplings. Flange couplings consist of two flanges—one attached to each shaft—that are bolted together, providing a strong and durable connection suitable for high-torque applications such as industrial gearboxes and heavy machinery. Sleeve couplings, also known as muff couplings, use a cylindrical sleeve that fits over the ends of both shafts and is secured with keys or set screws; they are lightweight and cost-effective, making them ideal for small-scale equipment with low torque requirements. Clamp couplings, or split couplings, feature a split sleeve that can be tightened around the shafts without disassembling the system, offering ease of installation and maintenance.