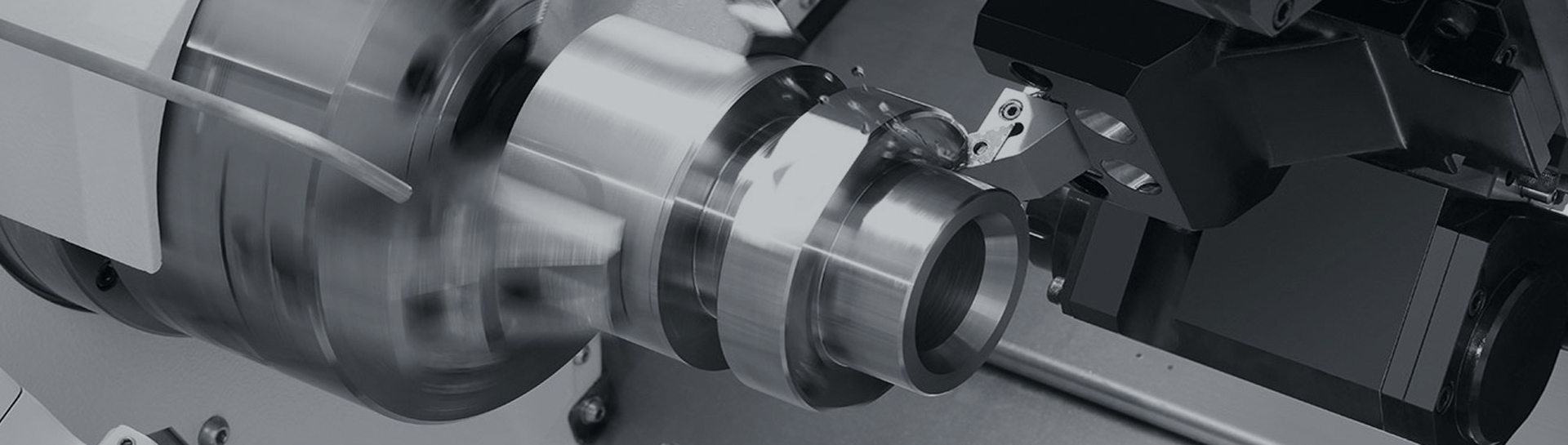
Drum gear coupling, also known as crowned tooth gear coupling, is a specialized type of flexible gear coupling designed to accommodate significant misalignment while transmitting high torque. Unlike conventional straight-tooth gear couplings, drum gear couplings feature curved or crowned teeth that provide enhanced misalignment capabilities and improved load distribution. This design innovation makes them particularly suitable for heavy-duty industrial applications where both high torque transmission and misalignment compensation are critical requirements.
The unique tooth profile of drum gear couplings allows for angular misalignment up to 1.5 degrees and parallel misalignment up to several millimeters, depending on the coupling size and design. This flexibility, combined with their high torque capacity, makes them ideal for connecting large rotating equipment such as turbines, compressors, pumps, and rolling mills.
Design Features and Construction
A typical drum gear coupling consists of two hubs with external crowned teeth and two sleeves with internal straight teeth. The hubs are mounted on the driving and driven shafts, while the sleeves connect the hubs and transmit torque through the meshing gear teeth. The crowned tooth profile is the key design element that distinguishes drum gear couplings from standard gear couplings.
The curvature of the crowned teeth allows for continuous tooth contact even when the shafts are misaligned. This design ensures that the load is distributed over multiple teeth, reducing stress concentration and increasing the coupling's service life. The tooth profile is typically designed with a specific radius of curvature that optimizes the contact pattern under various misalignment conditions.
Drum gear couplings are usually manufactured from high-strength alloy steels, with the teeth hardened through heat treatment processes such as carburizing or induction hardening. This provides excellent wear resistance and fatigue strength, enabling the coupling to withstand high cyclic loads and shock loads. The internal components are often lubricated with grease or oil to reduce friction and wear, and some designs incorporate sealing systems to prevent lubricant leakage and contamination.
Working Principle and Performance Characteristics
The working principle of drum gear coupling is based on the meshing of crowned external teeth on the hubs with straight internal teeth on the sleeves. When torque is applied, the teeth engage and transmit power from the driving hub to the driven hub through the sleeves. The crowned tooth design allows the teeth to slide relative to each other when misalignment occurs, accommodating angular, parallel, and axial misalignment simultaneously.
One of the significant advantages of drum gear couplings is their ability to maintain constant velocity transmission even under misalignment conditions. Unlike universal joints that cause speed fluctuations, drum gear couplings provide smooth power transmission with minimal vibration. This characteristic makes them particularly valuable in applications where speed consistency is critical, such as in paper mills, steel mills, and power generation equipment.
The flexible nature of drum gear couplings also helps in absorbing shock loads and dampening torsional vibrations. When sudden torque spikes occur, the slight movement between the crowned teeth allows the coupling to act as a shock absorber, protecting the connected equipment from damage. This capability is especially important in applications with frequent starts and stops or where load variations are common.
Applications and Selection Considerations
Drum gear couplings are widely used in various heavy industries due to their high torque capacity and excellent misalignment capabilities. Common applications include turbine-generator sets, large compressors, high-power pumps, rolling mills, marine propulsion systems, and mining equipment. They are particularly suitable for applications where space constraints prevent perfect alignment or where thermal expansion causes shaft movement during operation.
When selecting a drum gear coupling, several factors must be considered. The maximum torque requirement, including peak and shock loads, determines the coupling size and torque rating. The operating speed range must be within the coupling's rated speed, and the type and degree of expected misalignment should be compatible with the coupling's capabilities. Environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and the presence of corrosive substances influence material selection and lubrication requirements. Maintenance accessibility and lubrication intervals also play a crucial role in the selection process.
Proper installation and alignment are critical for the performance and longevity of drum gear couplings. While they can accommodate misalignment, operating within the manufacturer's specified limits ensures optimal performance and extended service life. Regular maintenance, including periodic lubrication and inspection for wear or damage, is essential to prevent unexpected failures and downtime.