1. Core Definition: A Versatile Rigid-Flexible Coupling
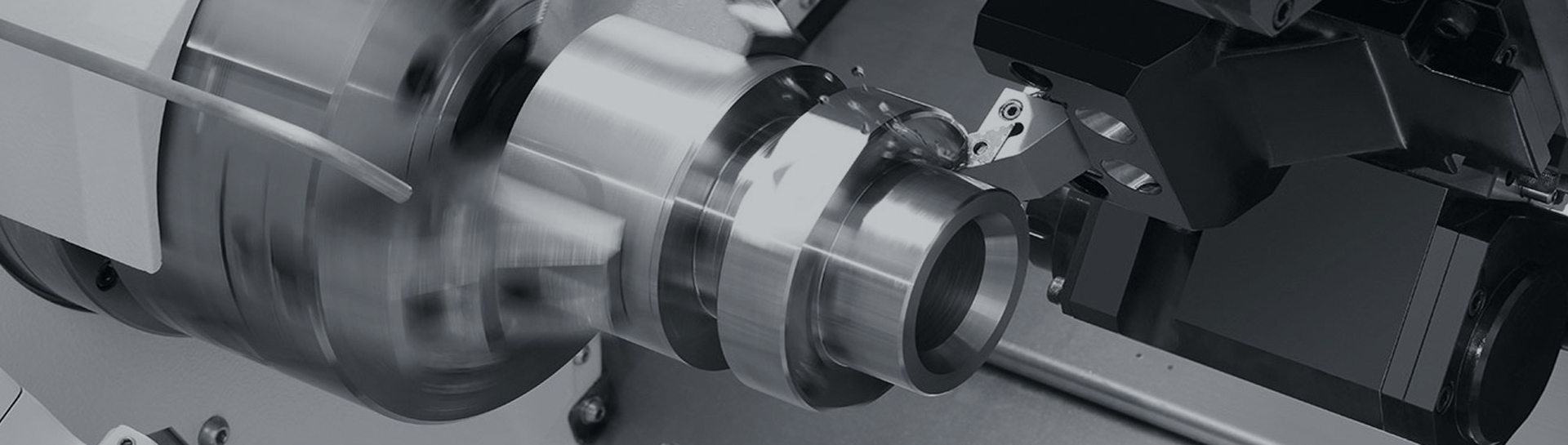
A Drum Gear Coupling is a high-performance rigid-flexible coupling engineered to transmit torque between two rotating shafts while compensating for axial, radial, and angular misalignments. Distinguished by its spherical-curved tooth profile, this coupling bridges the gap between rigid couplings (high torque capacity) and flexible couplings (misalignment tolerance), making it a critical component in heavy-duty industrial transmission systems worldwide. Unlike straight-tooth couplings, its drum-shaped gear design eliminates edge contact stress and enhances load distribution, enabling stable operation under fluctuating working conditions.
2. Structural Composition: Precision-Engineered Components
The coupling consists of four key interconnected parts, each optimized for durability and performance:
External Gear Sleeve: The core torque-transmitting element with a spherical-curved tooth top. This unique geometry expands contact area with the internal gear ring, improving load-bearing capacity and misalignment adaptability. High-quality sleeves are forged from alloy steel and undergo carburizing-quenching for surface hardness.
Internal Gear Ring: Matches the external sleeve’s tooth count and profile, forming a precision mesh to transfer power. It is typically mounted on the driven shaft and secured with flange bolts for rigidity.
Sealing System: A patented spherical sealing mechanism (adopted in advanced models like RWC series) prevents lubricant leakage and contaminant ingress. This design enables "one-time grease filling" maintenance, eliminating the need for frequent lubrication—critical for overhead or hard-to-reach installations.
End Covers & Fasteners: Protect internal components from dust and moisture while securing the assembly. Standardized bolts across adjacent models allow interchangeability, simplifying installation and replacement.
3. Working Principle: Torque Transmission with Misalignment Compensation
The coupling operates through three coordinated mechanisms:
Torque Transfer: When the driving shaft rotates, the external gear sleeve’s curved teeth engage with the internal gear ring, transferring rotational force to the driven shaft. The large pressure angle design (optimized in modern models) ensures efficient power transmission with minimal energy loss.
Misalignment Adaptation: As shafts deviate axially (up to several millimeters), radially (up to 0.5mm), or angularly (up to 1°30'), the spherical tooth profile slides smoothly along the internal gear ring. This eliminates 附加 loads on bearings and extends equipment lifespan—an improvement of 50% in angular tolerance compared to straight-tooth couplings.
Lubrication Retention: The sealed cavity retains grease, reducing tooth wear to 10% of that in grease-starved systems. For high-heat applications (e.g., rolling mills), forced oil lubrication is integrated to dissipate frictional heat and prevent material degradation.
4. Performance Advantages: Surpassing Traditional Couplings
Drum Gear Couplings outperform alternatives in five key metrics:
Higher Torque Capacity: Under the same outer diameter, it carries 15-20% more torque than straight-tooth couplings. Advanced models like Rokee’s ball-drum coupling boost load capacity by over 30% versus standard DC-series products.
Superior Misalignment Tolerance: Accommodates angular deviations up to 1°30' (vs. 1° for straight-tooth designs) and radial offsets without stress concentration.
Efficient & Quiet Operation: The curved tooth mesh reduces vibration and noise, achieving a transmission efficiency of 99.7%. This makes it suitable for precision equipment requiring low operational disturbance.
Low Maintenance: Sealed designs and wear-resistant materials extend maintenance intervals. Some models feature electronic wear alarms that trigger alerts when components reach end-of-life, preventing unexpected failures.
Compact Design: A reduced length-to-diameter ratio and lightweight alloy construction minimize rotational inertia, improving system responsiveness and energy efficiency.
5. Application Fields: Industrial Workhorses
The coupling excels in harsh, high-load environments across industries:
Metallurgy & Mining: Used in rolling mills, crushers, and ball mills. Its ability to withstand radial loads and temperature fluctuations makes it ideal for continuous production lines.
Heavy Machinery: Critical for port cranes, construction equipment, and large-scale elevators. RWC-series couplings, for example, are specifically engineered for port lifting applications with explosion-proof compliance.
Power & Manufacturing: Adapted for turbine generators, pump systems, and chemical reactors. For glass industry mixers, its multi-tooth contact design solves nonlinear stress issues in high-viscosity applications.
Agricultural & Specialized Equipment: Integrated into large irrigation pumps and greenhouse ventilation systems, where misalignment from structural settlement is common.